SHORTBOWL decanter centrifuge
Due to the special geometry of the rotating parts, the SHORTBOWL decanter centrifuge - solid bowl is best suited for separating fine solid particles with a high specific density difference to the liquid phase.
The Earth’s resources are finite. For decades, knowledge of this scarcity of resources and raw materials has led to the sustainable recovery of recyclable materials, which are then returned to the value chain.
Water is particularly significant here.
Only 2.5% of the water on Earth is fresh water. Only a small part is really accessible to humanity, namely 0.3% (in lakes, rivers and reservoirs).
But demand for high-quality water is increasing, driven by ecological changes, environmental factors, the growing world population, and increasing urbanization. This fact has led to greater environmental awareness worldwide regarding the availability and quality of water. As a result, there are increasingly stringent government regulations regarding the disposal of industrial wastewater.
Due to scarce water resources, and rising costs for water treatment and wastewater disposal, the use and conservation of water is a key issue in the manufacturing industry around the world. The focus here is often on repeatedly using treated water and reducing wastewater volumes, and even on avoiding wastewater entirely. Demand for new and increasingly efficient recycling technologies is growing, especially in regions that have limited access to available water sources and wastewater disposal options.


In order to increase the environmental friendliness of industrial plants, ZLD is used in a wide variety of fields, e.g. in power generation, and in the steel and chemical industries.
ZLD improves the environmental and economic footprint of a plant. Firstly by reusing water, and secondly by avoiding the discharge of wastewater, which could incur high costs or damage the environment. In this way, ZLD helps companies comply with strict regulations and guidelines regarding wastewater disposal and water reuse, as well as protecting the local environment.
In addition, ZLD enables the recovery of valuable resources from wastewater, which can be reused in the industrial process or sold.
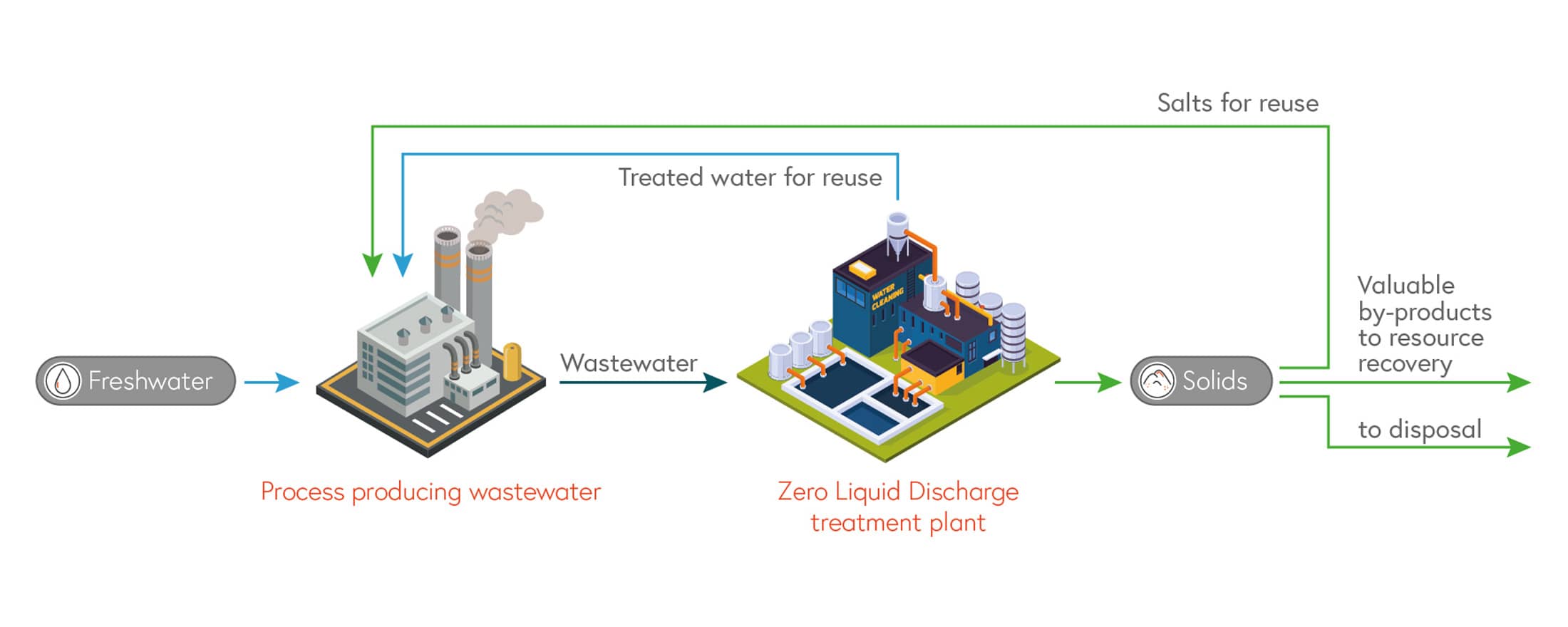
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is a treatment process focused on the economical reduction of wastewater. This produces clean water suitable for reuse, saving money and protecting the environment.
ZLD systems utilize advanced wastewater/ desalination technologies to treat and recycle virtually all the wastewater generated. In this process, the components dissolved in the water are converted into reusable solids such as sludge and salt. Different technologies are typically combined, such as thermal evaporation, crystallization, desalination and drying, and centrifugal separation.
The first step is to filter or precipitate waste and chemicals that are easy to remove. The wastewater is then concentrated by means of evaporation. In the third step, the concentrated waste stream is fed into a crystallizer.
In the last and decisive step, this suspension of water and crystallized solid is separated using a centrifuge. The efficiency of the upstream steps matters little; it is the use of the right centrifuge that determines the overall efficiency of the plant.
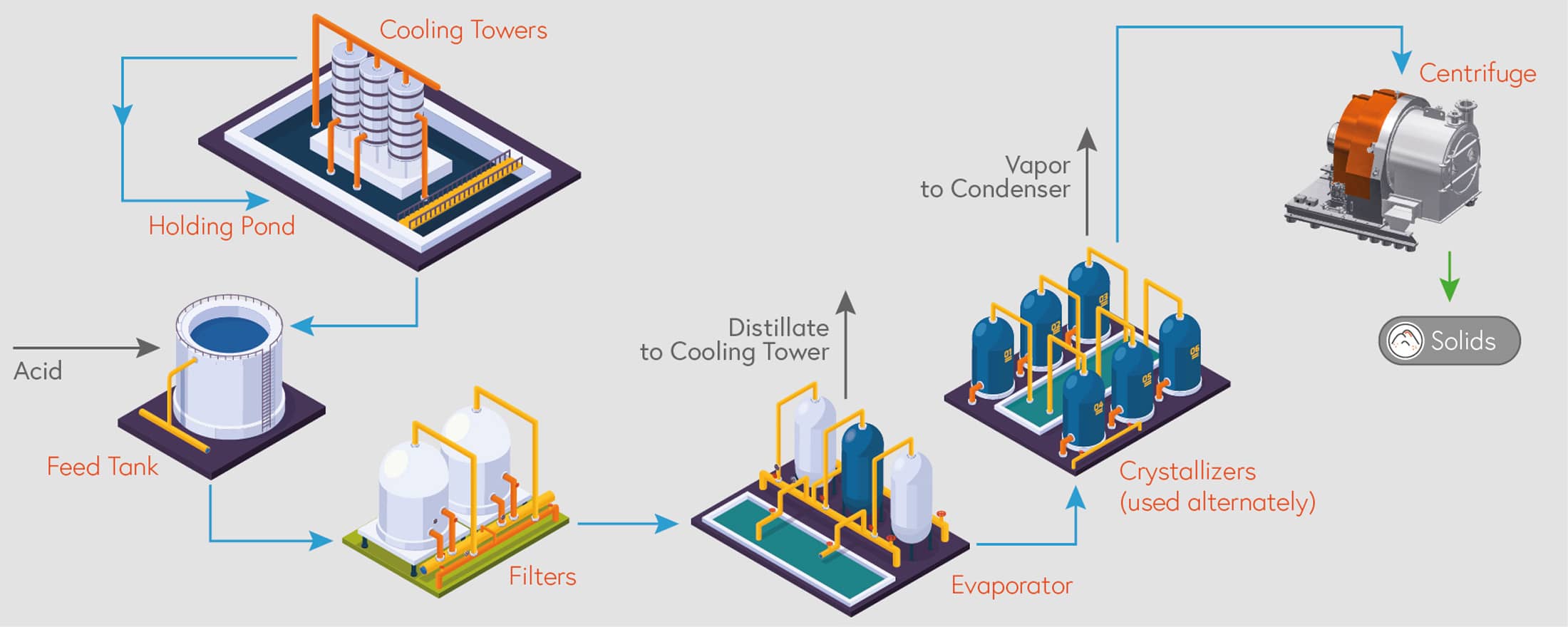
Solid-liquid separation is the critical final step in most ZLD processes, as this is where the remaining water is separated from the solids, in most cases salts. Dewatering is mostly done with decanters, SHORTBOWL decanters, pusher centrifuges and CONTURBEX centrifuges. For dewatering coarse residue, our HSG vibratory centrifuges have proven effective.
Finer mixed salts from crystallization plants are centrifuged using downstream SHORTBOWL decanters, SHS pusher centrifuges and CONTURBEX centrifuges at temperatures sometimes exceeding 100°C. The high-alloy stainless steels, Hastelloy® and titanium materials required for these machines are provided with appropriate wear protection made of tungsten carbide, Stellite® or ceramic tiles.
SIEBTECHNIK TEMA centrifuges are specially optimized for the respective separation task. When selecting materials, austenitic and ferritic stainless steels have proven themselves in centrifuge construction for applications subject to normal stresses.
For processes in which abrasive materials are processed, the centrifuges must be provided with effective wear protection. Starting with hard coal processing, we have been continuously developing wear protection systems since 1922.
Our centrifuges can be equipped with highly developed wear protection systems made of e.g. tungsten carbide, Stellite® or ceramic tiles, to name but a few. Rubber coatings or matrix coatings have also proven themselves in various applications.
If required, our engineers develop new and efficient solutions in coating, bonding and joining technology for our customers worldwide.
Centrifuge components must not only withstand high forces, but also process-related stresses such as corrosion, wear and high temperatures. Cost and availability of materials also play an important role. Our customers select the necessary product-contacting materials according to these very specific requirements.
Duplex and high-alloy stainless steels, Hastelloy® and titanium materials for a wide variety of processes and stresses are part of our daily business in centrifuge construction. Our quality management has developed very detailed and cost effective processes for design, manufacturing processes and component testing based on European guidelines.
Typical sheet metal and forging materials for centrifuge wetted components include

Due to the special geometry of the rotating parts, the SHORTBOWL decanter centrifuge - solid bowl is best suited for separating fine solid particles with a high specific density difference to the liquid phase.

Our decanters are individual, functional and versatile. They offer highly efficient separation of even the finest solids with almost complete clarification of the liquid phase.

The SIEBTECHNIK TEMA SHS pusher centrifuge has established itself and proven itself as a modern high-performance unit in many industries.

The CONTURBEX is a continuously operating, filtering centrifuge with a very wide range of applications.

With the SIEBTECHNIK TEMA HSG vibrating centrifuge you can continuously centrifugally dewater the world's largest solids capacity of bulk materials.

Find the right contact for your region.
We have the right solution for every task. And if not, we’ll work with you to find one. Get in touch with us!
Our specialists will be happy to advise you individually on site or remotely, and are available to answer any questions you may have. Send us a message using our
