Decanter centrifuge – solid bowl
Our decanters are individual, functional and versatile. They offer highly efficient separation of even the finest solids with almost complete clarification of the liquid phase.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a thermoplastic polymer made primarily from vinyl chloride monomers. It is one of the most widely used polymers in the world and has a variety of applications in different industries.
PVC plastics are divided into rigid and flexible PVC. These are used in a wide range of applications depending on their different properties. In the production of soft PVC, plasticizers are added to give the plastic elastic properties.
Firstly, it is durable and long-lasting, as PVC is weather resistant and has a long service life, making it a popular material for the manufacture of building components such as window frames, gutters, pipes and flooring.
PVC has high chemical resistance to water, acids, alkalis and many other chemicals, making it a suitable material for applications in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
PVC is fire-resistant, has a low fire hazard and produces little smoke and propellant gas when burned, making it a safe material for the manufacture of electrical cables and other electrical applications.
In addition, PVC is a cost-effective material because it is easy to manufacture and process.
PVC is environmentally friendly as it can be recycled and has a low environmental impact as it does not produce harmful chemicals or emissions.
PVC has a wide range of applications in various industries such as construction, automotive, textile, medical and electronics.
PVC is a very flexible material. It can be produced in many shapes and sizes and has good flexibility, making it a suitable material for the production of flexible products such as hoses, films and textiles.
Few materials adapt as flexibly to the diverse needs of the construction industry as plastic. Plastics are increasingly replacing traditional materials such as wood and metal.
PVC has a high chemical resistance and is resistant to water, oil and many acids and alkalis. It also has good mechanical strength and durability. These properties make it a popular material for making water and sewer pipes, gutters, front doors, window frames and sills, flooring and other building components.
It is also used in electrical engineering, particularly in the manufacture of insulation and electrical cable sheathing.
In the automotive industry, PVC is used to make interior trim, seat covers and headliners.
It is also an important material in the manufacture of medical equipment, particularly blood transfusion and dialysis systems. High-purity PVC with very low levels of additives and impurities is used in medical applications. Advantages include good thermoformability, strength, flexibility, chemical resistance and low allergy potential. PVC is used to make bags for blood, drugs or nutritional solutions, gloves, tubing and catheters, blister packs and various disposable items.
PVC is also used in the textile industry, particularly in the manufacture of shoes, bags and clothing. It is also used as a plasticizer in many other materials, such as rubber and polyurethane, to improve their flexibility and durability.
PVC has a wide range of applications, including the packaging and sports and leisure industries. For example, it is used for films, packaging, tents, suitcases, artificial leather and as a substrate for advertising media.
Overall, PVC is a versatile and important material with many applications in different industries. It is valued for its chemical resistance, durability and mechanical properties and has proven to be a reliable material for many applications.
PVC is made by polymerizing vinyl chloride monomer (VCM). The VCM is polymerized in a reaction in the presence of an initiator (usually peroxide) and a stabilizer. This process can be either suspension or emulsion polymerization.
In emulsion polymerization, the monomers are emulsified in water and polymerized under pressure and at lower temperatures. This process produces PVC dispersions, which are then dried and milled.
The resulting PVC powder is then shaped and thermally treated. This process is called calcination. There are several types of calcination, depending on the application and production method.
After calcination, the PVC is further processed into its final form, either by extrusion, injection molding, pressing or other technologies.
The most commonly used process for producing polyvinyl chloride is the slurry process.
In suspension polymerization, the monomers are suspended in water and polymerized under pressure and at high temperatures. Organic peroxides are typically used as initiators. This process produces PVC particles, which are then dried, ground and screened.
The resulting product is also known as S-PVC.
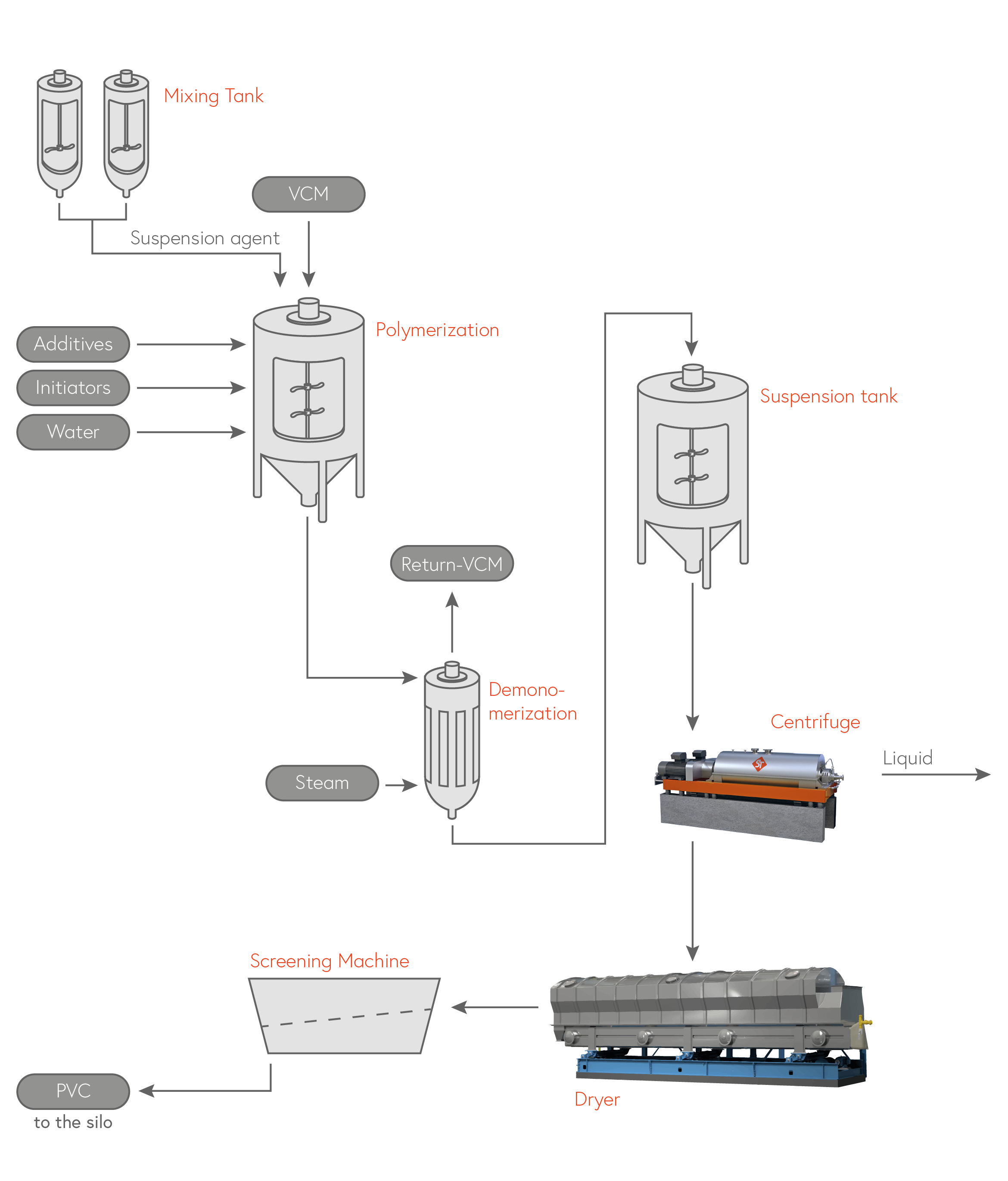
PVC production – suspension process
Centrifuges are used in the production of PVC to remove excess liquid and solvent from the PVC powder. This step is called drying and is important for the quality and performance of the final PVC product.
Compared to other alternatives, centrifuges are able to remove large amounts of liquid and solvent in a short period of time, dry the powder evenly and maintain the moisture content of the powder within certain tolerances. They also allow PVC powder to be dried under closed conditions, helping to reduce production costs and improve product quality.
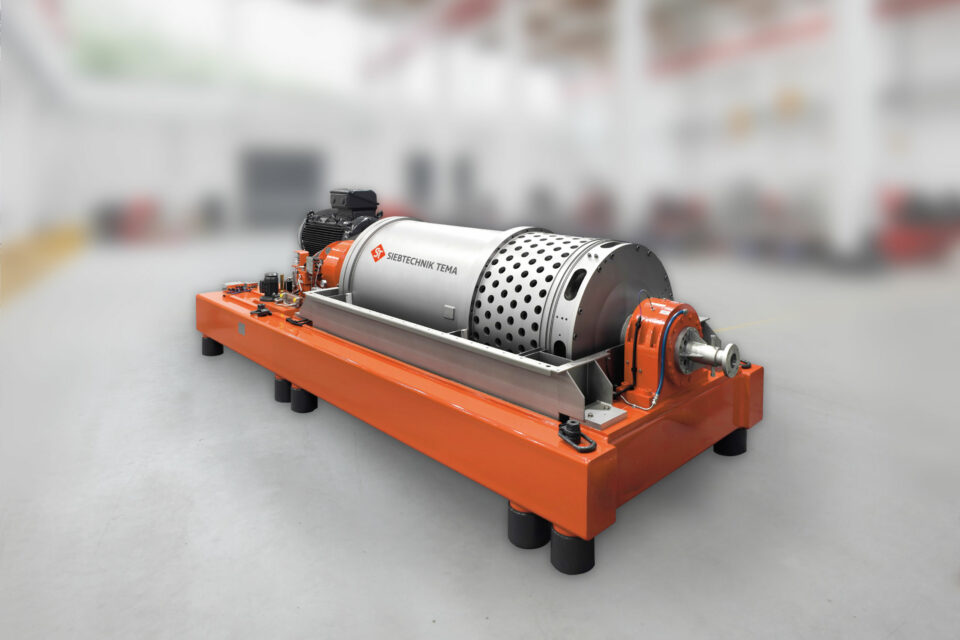
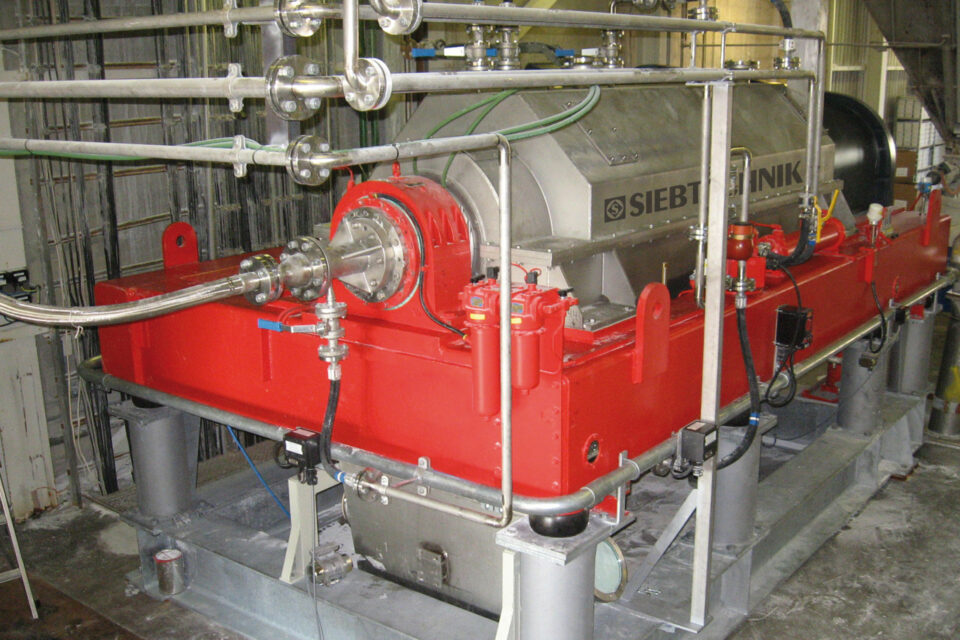


Centrifuge components must not only withstand high forces, but also process-related stresses such as corrosion, wear and high temperatures. Cost and availability of materials also play an important role. Our customers select the necessary product-contacting materials according to these very specific requirements.
Duplex and high-alloy stainless steels, Hastelloy® and titanium materials for a wide variety of processes and stresses are part of our daily business in centrifuge construction. Our quality management has developed very detailed and cost effective processes for design, manufacturing processes and component testing based on European guidelines.
Typical sheet metal and forging materials for centrifuge wetted components include

Our decanters are individual, functional and versatile. They offer highly efficient separation of even the finest solids with almost complete clarification of the liquid phase.

Due to the special geometry of the rotating parts, the SHORTBOWL decanter centrifuge - solid bowl is best suited for separating fine solid particles with a high specific density difference to the liquid phase.

It combines the process engineering advantages of a sedimenting decanter and a filtering centrifuge in one machine.

Find the right contact for your region.
We have the right solution for every task. And if not, we’ll work with you to find one. Get in touch with us!
Our specialists will be happy to advise you individually on site or remotely, and are available to answer any questions you may have. Send us a message using our
